LOS ANGELES ABRASION TEST:
This is hardness test for aggregates, used in Laboratory to determine the hardness value or abrasion value
APPARATUS :
Los Angeles Abrasion Testing Machine ,
Abrasive Charge – Cast iron or steel balls ,
Test sieve – 1.70 mm IS sieve ,
Balance of capacity 10 kg , Oven , Tray
The aggregate used in surface course of the highway pavements are subjected to wearing due to movement of traffic.
When vehicles move on the road, the soil particles present between the pneumatic tyres and road surface cause abrasion of road aggregates.
The steel reamed wheels of animal driven vehicles also cause considerable abrasion of the road surface.
Therefore, the road aggregates should be hard enough to resist abrasion.
The principle of Los Angeles abrasion test is to produce abrasive action by use of standard steel balls which when mixed with aggregates and rotated in a drum for specific number of revolutions also causes impact on aggregates.
The percentage wear of the aggregates due to rubbing with steel balls is determined and is known as Los Angeles Abrasion Value.
Key point of los angles test:
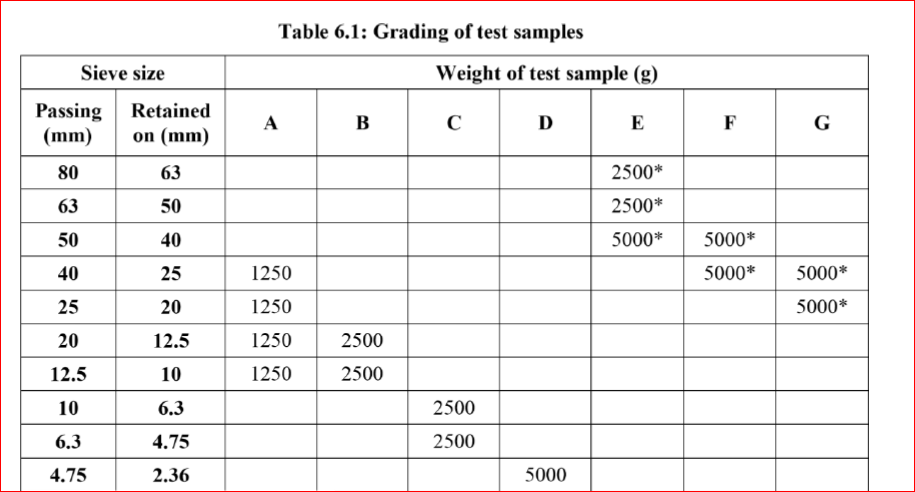
Rotate the machine at a speed of 30 – 33 revolutions per minute. The number of revolutions is 500 for grading A, B, C & D and 1000 for grading E, F & G. The machine should be
5 kg of sample for grading A, B, C & D and 10 kg for grading E, F & G
THE CALCULATION PART:
Original weight of aggregate sample = W1 g
Weight of aggregate sample retained = W2 g
Weight passing 1.7mm IS sieve = W1 - W2 g
Los Angeles Abrasion Value = (W1 - W2) / W1 X 100
Los angeles abrasion value should lies in below given range for different types of roads
Types of pavement layers Max. Permissible Abrasion Value in %
1:WBM , SUB BASE COURSE 60%
2:WBM BASE COURSE WITH BITUMEN SURFACE 50%
3: BITUMEN BOUND MACADAM 50%
4:WBM SURFACING COURSE 40%
5: BITUMINOUS PENETRATION MACADAM 40%
6:BITUMINOUS SURFACING DRESSING CEMENT
CONCRETE SURFACING COURSE 35%
7:BITUMINOUS CONCRETE SURFACING COURSE 30%